Can you imagine a walkie-talkie? A walkie-talkie that’s used for war emergencies?
A network is an important piece in the puzzle of technological development. It has a key function in communication between people and resources. Furthermore, it is a class of computers and devices that are so connected that they allow information to be exchanged between the parties involved.
Similarly, the Mobile Ad-Hoc Network is a temporary (ad-hoc) network of freely (mobile) moving nodes in a tech device that doesn’t need a centralized infrastructural network. The mobile network connects the nodes one by one, forming a chain of communication to send data packs and other useful information.

In this article, we will discuss MANET in terms of its
Basic Features
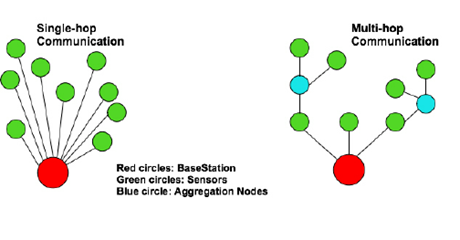
Multihop Routing
MANET system does have its useful applications but there are some challenges attached to it. MANET has a restricted wireless transmission range and a time-varying wireless link. Not much is transmitted as the network is mobile in nature. Such networks are also subject to obstruction and interference, affecting the data rate and consistency. Additionally, node movements can lead to errors and breakages. There are battery constraints that make the quality of service less satisfactory. Another challenge is security. It is one of the main challenges because data packets need to be transferred easily and safely to the other node.
Every system seeks one thing, and that is Security. As MANET is mainly fraught with security challenges, the solutions involve two approaches. One is proactive and the other is reactive. The proactive approach attempts to thwart threats through cryptographic techniques while the reactive approach seeks to detect threats and act accordingly. For example, most secure routing protocols adopt a proactive approach to secure routing messages while the reactive approach is used for protecting packet forwarding operations.
In the ideal scenario, both approaches should be applied as per the requirement. These approaches need to incorporate prevention, detection, and reaction.
When it comes to prevention, it is said that deterring the attacker has been infeasible when it comes to MANET as mobile devices are prone to compromise or physical sturdiness. Therefore, the detection and reaction component work for occasional intrusions.
In MANET, the prevention component is mainly achieved by secure ad-hoc routing protocols that prevent the attacker from installing incorrect routing states at other nodes.
Ad Hoc Protocols such as DSR (2), AODV (1), and Destination-Sequenced Distance Vector (DSDV), and employ different cryptographic primitives for example, HMAC, digital signatures, hash chains) are used to authenticate the routing messages.
The detection part identifies abnormal behaviour by malicious nodes. Such a thing is observed in an end-to-end manner or by neighboring nodes through overhearing.
Once the detection is identified, the reaction component sees adjustments in routing and forwarding operation, ranging from avoiding the node in route selection to collectively excluding the node from the network.
MANET is an emerging technology that has its benefits and at the same time challenges. Therefore, the applications of MANET are very useful whereas the security component can be tackled with some security mechanisms.